How does AI work: A beginner’s guide
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a multidisciplinary field that enables machines to mimic or replicate human cognitive functions such as learning, reasoning, perception, and decision-making. Though the concept may seem abstract or futuristic, the underlying mechanics of AI can be explained through a structured pipeline of data, models, and computation.
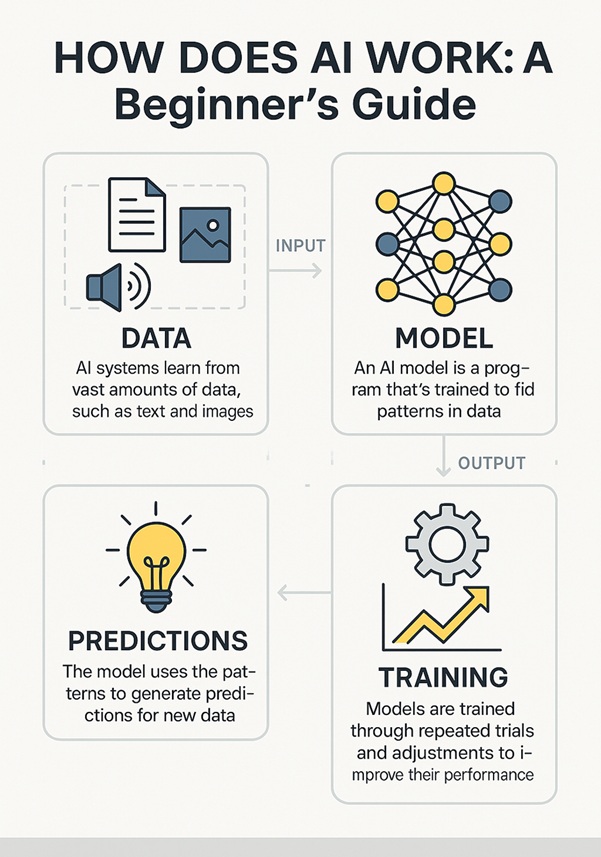
At its core, AI systems function through three primary components: data input, algorithms, and output generation.
- Data is the lifeblood of AI. Whether it’s text, images, audio, or sensor signals, all AI systems begin with collecting and organizing large volumes of data. This data is used to recognize patterns and relationships within a domain.
- The algorithm is the mathematical method that processes this data. Most modern AI systems rely on machine learning (ML)—a subset of AI where algorithms learn from data rather than being explicitly programmed. These models are trained using historical datasets to predict or classify future outcomes.
- Once trained, the model is evaluated and deployed to make inferences or decisions on new, unseen data. In real-time applications, this could mean recommending a product, recognizing a face, or navigating an autonomous vehicle.
The dominant paradigm today is deep learning, where neural networks—modeled loosely on the human brain—contain multiple layers of interconnected nodes (neurons). These systems are particularly effective for handling unstructured data such as images or speech.
AI systems may be further enhanced through feedback loops that allow them to improve over time (reinforcement learning), or through pretrained models that transfer knowledge across tasks (transfer learning).
Importantly, AI does not operate in a vacuum. It depends on infrastructure like high-performance computing, cloud platforms, and robust data pipelines. Additionally, explainability, fairness, and governance mechanisms are crucial for ensuring trustworthy AI deployment.
In essence, AI works by transforming data into decisions using mathematical logic, probabilistic reasoning, and learning systems. Understanding these mechanisms is essential for designing, evaluating, or regulating intelligent technologies in the real world.