What is Artificial Intelligence

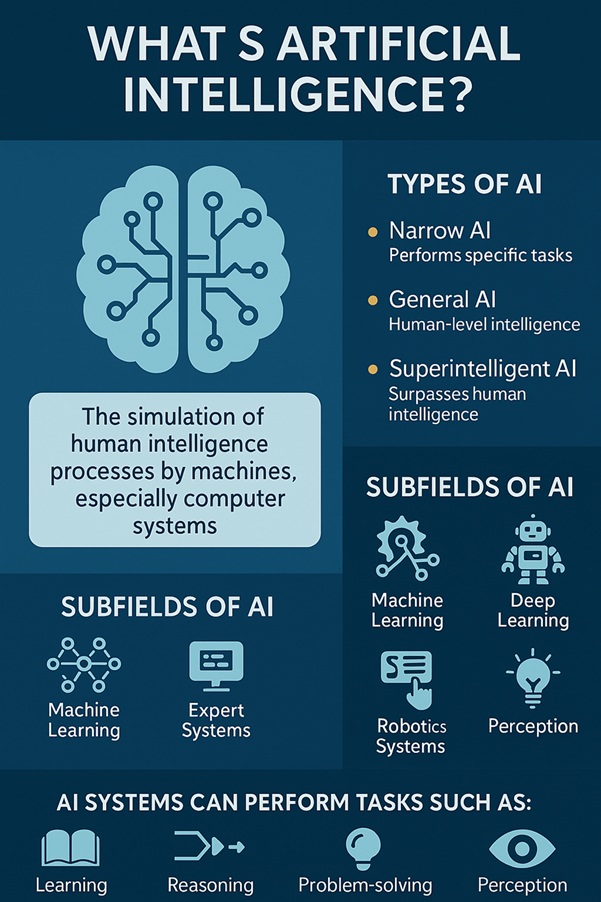
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the field of computer science focused on creating systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks include reasoning, learning, perception, problem-solving, decision-making, and natural language understanding. At its core, AI is about replicating — and in many cases enhancing — cognitive functions through algorithms, data, and computational power.
The concept is broader than often assumed. AI encompasses a wide spectrum of capabilities: from narrow AI (systems trained for specific tasks like image recognition or voice transcription) to the more theoretical general AI (machines with human-level reasoning across multiple domains). Most real-world AI systems today fall under narrow AI, yet their impact spans every major sector — healthcare, finance, manufacturing, education, logistics, and more.
AI can be categorized based on how it learns and acts. Machine Learning (ML) is the dominant paradigm where systems improve through exposure to data. Within ML, techniques such as supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning allow machines to generalize from examples, identify patterns, or learn optimal behavior through reward signals. On a more sophisticated level, Deep Learning — which uses multi-layered neural networks — powers many of today’s breakthroughs in computer vision, speech recognition, and generative AI.
What differentiates AI from traditional rule-based software is its adaptability. AI systems do not rely on hardcoded logic alone; instead, they model patterns from data and update behavior as new information becomes available. This shift from deterministic programming to probabilistic, data-driven modeling is transformative — but it also introduces new challenges in interpretability, bias, and control.
In essence, AI is not a singular technology but an evolving ecosystem of algorithms, models, and architectures. As we move deeper into the 21st century, understanding the foundations of AI is essential not just for technologists, but for business leaders, policymakers, and society at large. The question is no longer if AI will impact our world — but how deeply and how responsibly it will be integrated into it.