AI in medicine and healthcare: Coming of age?

The integration of Artificial Intelligence into healthcare has transitioned from “science fiction” to a cornerstone of modern clinical practice. As of 2026, the FDA has cleared over 1,200 AI-enabled medical devices, signaling that the technology has truly come of age.
Here are 20 real-world applications of AI in medicine today, backed by current data and industry examples.
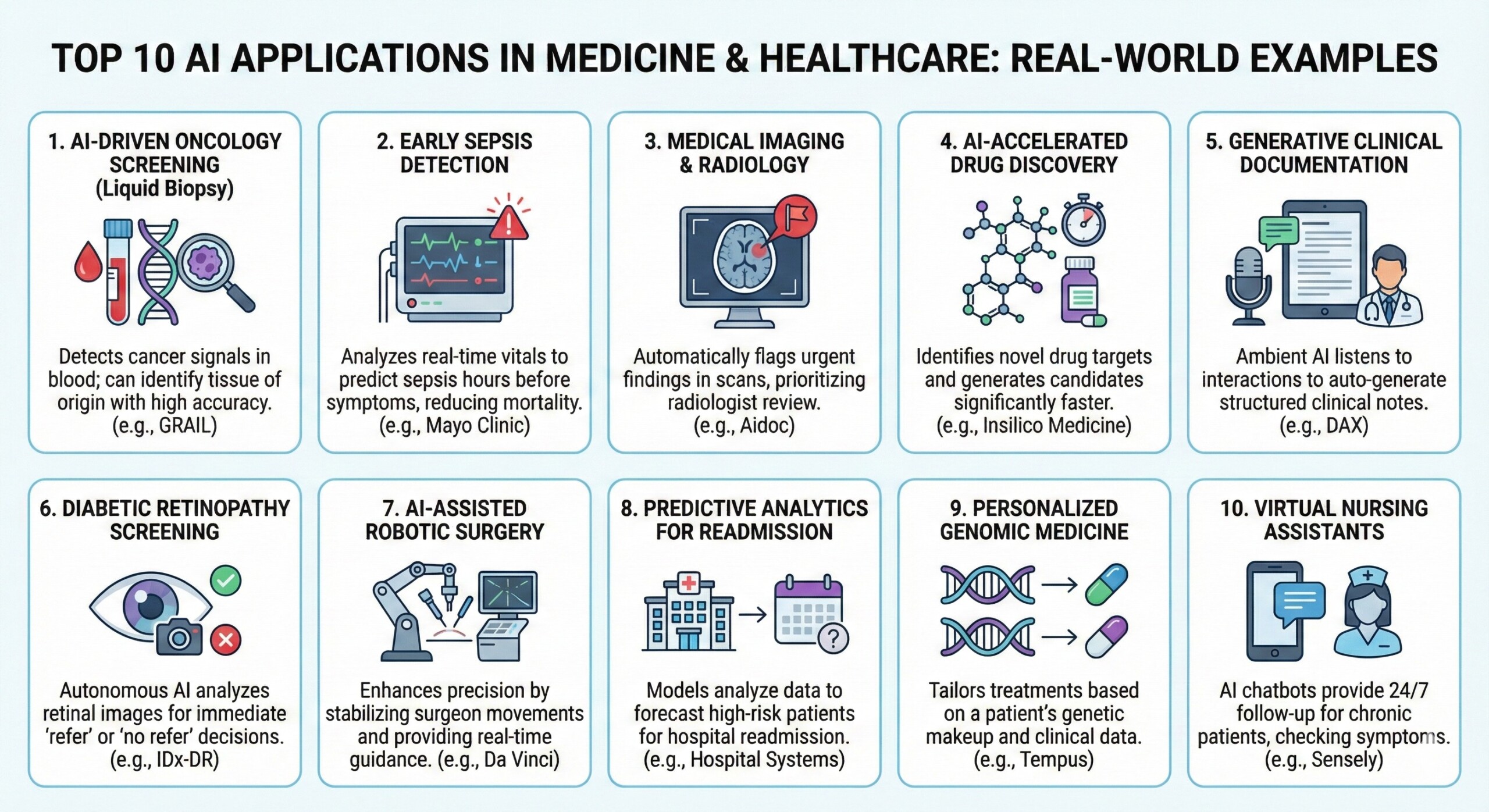
1. AI-Driven Oncology Screening (Liquid Biopsy)
Companies like GRAIL use AI to detect over 50 types of cancer from a single blood draw. Their Galleri test leverages machine learning to sift through billions of DNA regions to find “signals” of cancer before symptoms appear.
- Fact: The test can identify the tissue of origin with 90% accuracy when a cancer signal is detected.
2. Early Sepsis Detection
Sepsis is a leading cause of hospital deaths. AI models, such as those used by the Mayo Clinic, analyze real-time vital signs and lab results to predict sepsis hours before clinical symptoms manifest.
- Fact: AI-driven alerts have been shown to reduce sepsis mortality rates by as much as 18–20% in some health systems.
3. Medical Imaging & Radiology
AI is most mature in radiology. Algorithms from companies like Aidoc and Zebra Medical Vision automatically flag urgent findings—like brain bleeds or pulmonary embolisms—in CT scans, moving them to the top of a radiologist’s queue.
- Fact: Over 75% of FDA-cleared AI devices are currently in the field of radiology.
4. AI-Accelerated Drug Discovery
Historically, it takes 10 years and $2.6 billion to bring a drug to market. AI platforms like Insilico Medicine have identified novel drug targets and generated drug candidates in under 50 days.
- Fact: In 2025, Rentosertib, the first generative-AI drug candidate, entered Phase 2 clinical trials for pulmonary fibrosis.
An excellent collection of learning videos awaits you on our Youtube channel.
5. Generative Clinical Documentation
Ambient AI assistants, such as Microsoft’s Dragon Ambient eXperience (DAX), listen to patient-doctor conversations and automatically generate structured clinical notes in the EHR (Electronic Health Record).
- Fact: Clinicians using these tools report a 50% reduction in documentation time, significantly lowering burnout.
6. Diabetic Retinopathy Screening
AI tools like IDx-DR allow non-specialists to screen patients for diabetic retinopathy (a leading cause of blindness) using a retinal camera. The AI provides an immediate diagnostic “refer” or “no refer” decision without a doctor’s manual review.
7. AI-Assisted Robotic Surgery
The Da Vinci Surgical System and newer platforms use AI to stabilize a surgeon’s hand movements and provide real-time guidance during minimally invasive procedures.
- Fact: AI-integrated robotics can reduce “tissue trauma” and shorten hospital stays by improving surgical precision.
8. Predictive Analytics for Patient Readmission
Hospitals use AI models to analyze social determinants of health (e.g., housing, transportation) and clinical data to predict which patients are at high risk for readmission within 30 days.
- Fact: This allows for personalized “post-discharge” care plans, saving hospitals millions in penalties. A constantly updated Whatsapp channel awaits your participation.
9. Personalized Genomic Medicine
Platforms like Tempus use AI to analyze a patient’s genetic makeup alongside clinical data to recommend the most effective chemotherapy or immunotherapy.
- Fact: This shifts medicine from “one size fits all” to “precision oncology.”
10. Virtual Nursing Assistants
AI-powered chatbots and voice assistants (e.g., Sensely) provide 24/7 follow-up for chronic patients, checking symptoms and ensuring medication adherence.
- Fact: These systems can triage patients, directing only the “high-risk” cases to human nurses, reducing system load.
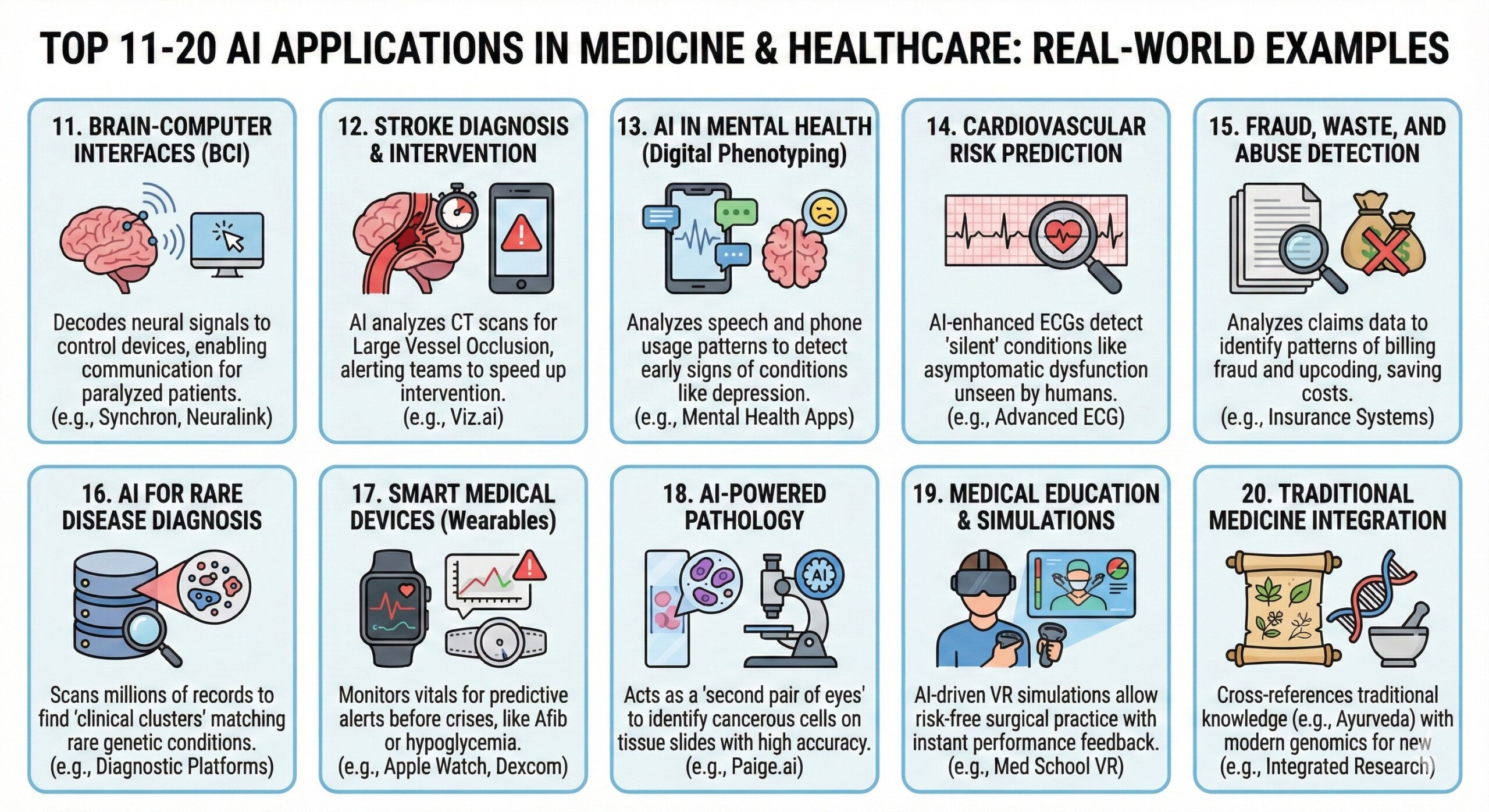
11. Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCI)
AI is being used to decode neural signals in patients with paralysis. Systems from companies like Synchron or Neuralink allow patients to control digital cursors or robotic limbs using only their thoughts.
- Fact: In 2024–2025, BCIs achieved a record-breaking 60+ words-per-minute for speech-impaired patients.
12. Stroke Diagnosis and Intervention
AI tools like Viz.ai analyze CT scans for signs of “Large Vessel Occlusion” (LVO). If a stroke is detected, the AI automatically alerts the entire neurosurgical team on their mobile phones simultaneously.
- Fact: This can save up to 66 minutes in the “door-to-needle” time, which is critical since “time is brain.” Excellent individualised mentoring programmes available.
13. AI in Mental Health (Digital Phenotyping)
Apps are now using AI to analyze speech patterns and smartphone usage (typing speed, sleep patterns) to detect early signs of depression or manic episodes in bipolar patients.
14. Cardiovascular Risk Prediction
AI-enhanced ECGs can now detect “silent” heart conditions, such as asymptomatic left ventricular dysfunction, which a human doctor cannot see on a standard rhythm strip.
15. Fraud, Waste, and Abuse Detection
AI algorithms analyze millions of medical insurance claims to spot patterns of “upcoding” or fraudulent billing, saving the healthcare system billions of dollars annually.
16. AI for Rare Disease Diagnosis
On average, rare disease patients wait 5 years for a diagnosis. AI platforms can scan millions of medical records to identify “clinical clusters” that match rare genetic conditions, shortening the “diagnostic odyssey.” Subscribe to our free AI newsletter now.
17. Smart Medical Devices (Wearables)
Wearables like the Apple Watch or Dexcom G7 use AI to monitor heart rhythms for Afib or glucose levels for diabetes, providing predictive alerts before a crisis (e.g., hypoglycaemia) occurs.
18. AI-Powered Pathology
Digital pathology platforms (e.g., Paige.ai) use AI to identify cancerous cells on tissue slides. The AI acts as a “second pair of eyes” to ensure no microscopic tumour cells are missed.
19. Medical Education & Simulations
AI-driven virtual reality (VR) simulations allow medical students to practice complex surgeries in a risk-free environment, with the AI providing instant feedback on their technique.
20. Traditional Medicine Integration
In countries like India, AI is being used to catalogue thousands of years of traditional knowledge (Ayurveda) and cross-reference it with modern genomics to find new herbal-based treatments for modern diseases. Upgrade your AI-readiness with our masterclass.
The Verdict: Is it “Coming of Age?”
Yes. In 2026, AI is no longer a peripheral experiment; it is the “operating system” for the next generation of healthcare. While challenges regarding data privacy and “algorithmic bias” remain, the shift toward augmented intelligence – where machines handle the data and humans handle the care – is now the industry standard.








